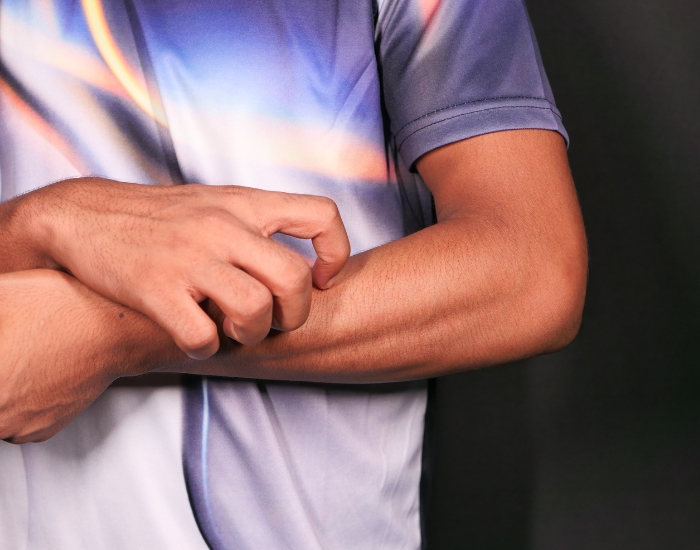
Persistent itching, medically known as pruritus, can be a frustrating and uncomfortable symptom. While itching can be caused by many factors, its presence in conjunction with liver problems often signals something more serious. For individuals with liver conditions, such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, or other forms of liver disease, the skin’s constant itching can be an indicator of internal complications. If you’re experiencing persistent itching, understanding its connection to liver health is crucial.
Why Persistent Itching May Signal Liver Problems
Liver disease affects many bodily systems, including the skin. The liver plays a vital role in detoxifying the body by processing waste and filtering toxins from the blood. When liver function declines, these toxins can build up in the bloodstream, leading to a condition called cholestasis, where the flow of bile is impaired. This bile buildup can cause itching, particularly on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
In addition to cholestasis, liver disease can lead to an imbalance in bile acids and other substances that affect skin health, causing intense itching. This symptom often worsens at night and may become so severe that it interferes with daily life.
Other Symptoms of Liver Health Issues
While persistent itching can be an early sign of liver trouble, it is rarely the only symptom. People with liver conditions may also experience:
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to a buildup of bilirubin.
- Fatigue: A feeling of exhaustion or weakness that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Swelling: Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen or legs.
- Dark Urine & Pale Stools: Unusual changes in the color of your urine and stool.
If these symptoms accompany your itching, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly, as they may indicate liver damage that requires immediate care.
Managing Itching Linked to Liver Disease
Managing itching related to liver conditions often involves addressing the underlying liver disease and relieving the discomfort associated with pruritus. Here are some approaches to consider:
- Medications: Certain medications, such as bile acid binders and antihistamines, may be prescribed to reduce itching. In severe cases, doctors may recommend a drug like cholestyramine to improve bile flow.
- Moisturizing Lotion: Regularly applying moisturizing lotion can help soothe dry, irritated skin and may reduce itching.
- Avoiding Triggers: If you know certain factors like heat or sweating worsen your itching, try to avoid them when possible.
- Maintaining Liver Health: If liver disease is the underlying cause, managing it with the help of a healthcare provider is essential. This may involve lifestyle changes, medications, and monitoring liver function through regular tests.
When to Seek Medical Help
If persistent itching is becoming more frequent or severe, especially when accompanied by other symptoms such as jaundice or swelling, it’s crucial to seek professional care. Left untreated, liver conditions can worsen, leading to complications such as liver failure or cirrhosis.
At Copperfield Family Clinic, we specialize in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and can help determine whether your itching is linked to a liver issue. Our expert physicians will work with you to assess your liver health and provide a personalized treatment plan designed to improve your quality of life.
Final Thoughts
Persistent itching can be more than just an irritating symptom; it may be an early warning sign of liver problems that require attention. If you’re experiencing this symptom or suspect your liver health is at risk, don’t wait to seek help. Early diagnosis and management of liver disease can significantly improve outcomes and prevent further complications.
At Copperfield Family Clinic, our compassionate team is here to provide you with the care and support you need to address any liver health concerns. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward better health.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this blog is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. It should not be used to diagnose or treat any health condition. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment of any symptoms or medical concerns.